Percentage Calculator Find Increase & Decrease %
What is the percentage increase/decrease
Calculating percentages is something we all face in daily life — whether it’s checking exam marks, figuring out a salary or loan increase, tracking profit and growth, or even working out the off price during a sale. The problem is that manual percentage calculations can often feel confusing: What is the right formula? How do you quickly find the percentage difference, increase, or decrease without making mistakes?
That’s where an online Percentage Calculator becomes the perfect solution. With just a few clicks, you can instantly find percentages, calculate increases or reductions, and solve problems like Quick grade percentage, salary growth, or loan interest without stress. Our smart percentage calculator is designed to save time, avoid errors, and give accurate results — making percentage math simple for everyone.
What is Percentage Calculator?
Use this all-in-one percentage calculator to answer questions like “What percent of X is Y?”, “What is P% of X?”, “X is P% of what?”, and “How does a value change after an increase or decrease by P%?”
It’s built for real life—marks, discounted price (off price), profit, growth, salary raise, loan comparisons, and more. Just like a font generator helps you instantly create stylish text without effort, a percentage calculator quickly finds increases, decreases, and differences online with ease
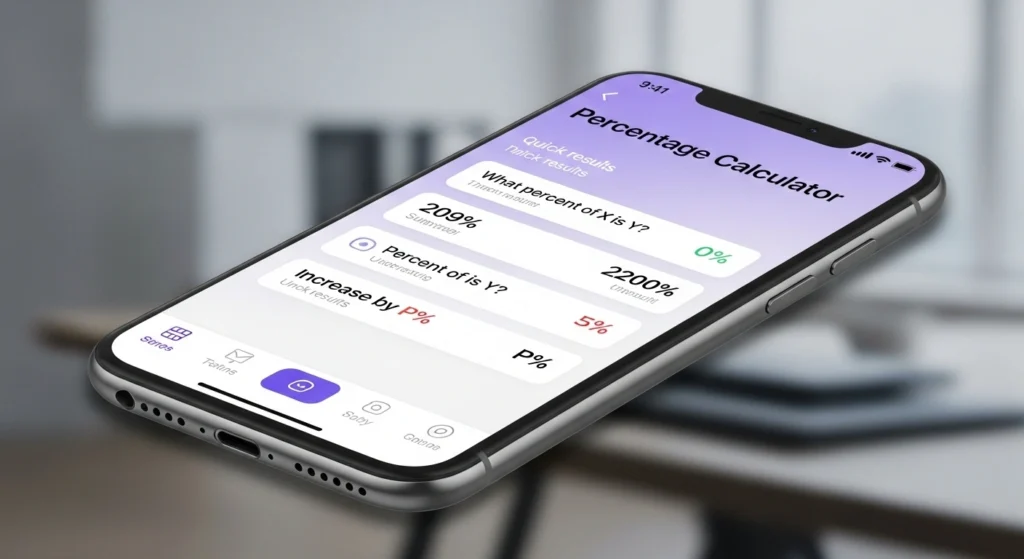
How to use the Percentage Calculator (4 quick modes)
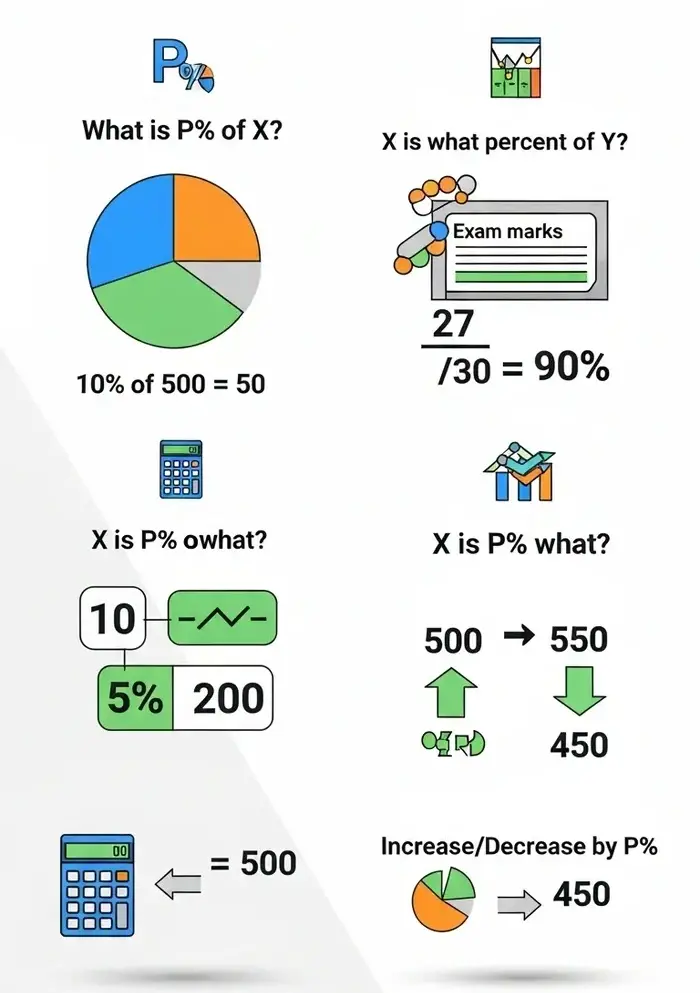
1. What is P% of X?
2. X is what percent of Y?
3. X is P% of what?
4. What is X increased/decreased by P%?
Tip: The tool solves any missing field automatically—type any two values, get the third.
Percentage Calculator cheat sheet (formulas & when to use)
| Problem | Use when | Formula | Mini example |
| What is P% of X? | Find a part of a whole | Y = (P/100) × X | 15% of 80 = 0.15 × 80 = 12 |
| X is what percent of Y? | Compare part to whole | P = (X ÷ Y) × 100 | 1245 rent of 4000 salary → 31.125% |
| X is P% of what? | Find the whole from part & percent | Y = X ÷ (P/100) | 10 is 5% of 200 |
| Increase by P% | Markups, growth, salary raise | New = X × (1 + P/100) | 100 ↑20% → 120 |
| Decrease by P% | Discounts, reduction, off price | New = X × (1 − P/100) | 200 ↓50% → 100 |
| Percent change | Old to new (baseline is old) | `((New − Old) ÷ | Old |
| Percent difference | Two values, no baseline | ` | a − b |
| Percent error | Experimental vs theoretical | ` | Exp − Theo |
Worked examples (step-by-step)
1) Exam marks:
. You scored 27 out of 30.
. Percent = 27 ÷ 30 × 100 = 90%.
2) Off-price discount:
. An item was $48.89 after 10% off. What was the original price?
. Original = 48.89 ÷ (1 − 0.10) = 48.89 ÷ 0.9 = 54.322… ≈ $54.32
3) Profit percentage:
. Bought for $420, sold for $525. Profit = 525 − 420 = $105.
. Profit % = 105 ÷ 420 × 100 = 25%.
4) Salary raise:
. Salary goes from $100,000 to $120,000.
. Percent change = (120,000 − 100,000) ÷ 100,000 × 100 = 20%.
5) Loan comparison (rate drop):
. APR drops from 14% to 12%.
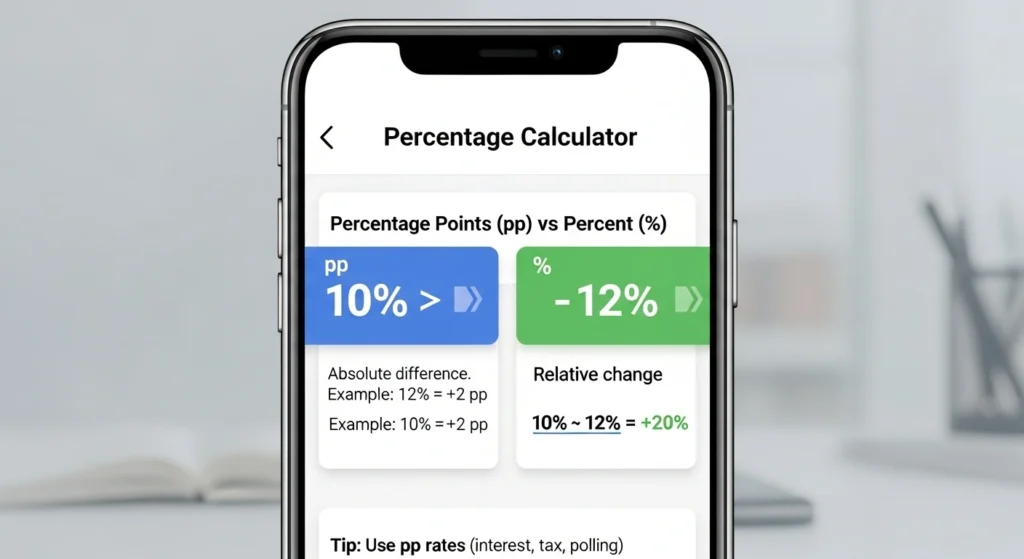
. Change = 2 percentage points (pp), not 2%.
. Relative change = (12 − 14) ÷ 14 × 100 = −14.29%.
6) Growth vs difference:
. Speed: 60 to 120. Percent change = (120 − 60)/60 × 100 = 100% (twice as fast).
. Percent difference of 60 vs 120 = |60 − 120| / ((60 + 120)/2) × 100 = 60 / 90 × 100 = 66.67%.
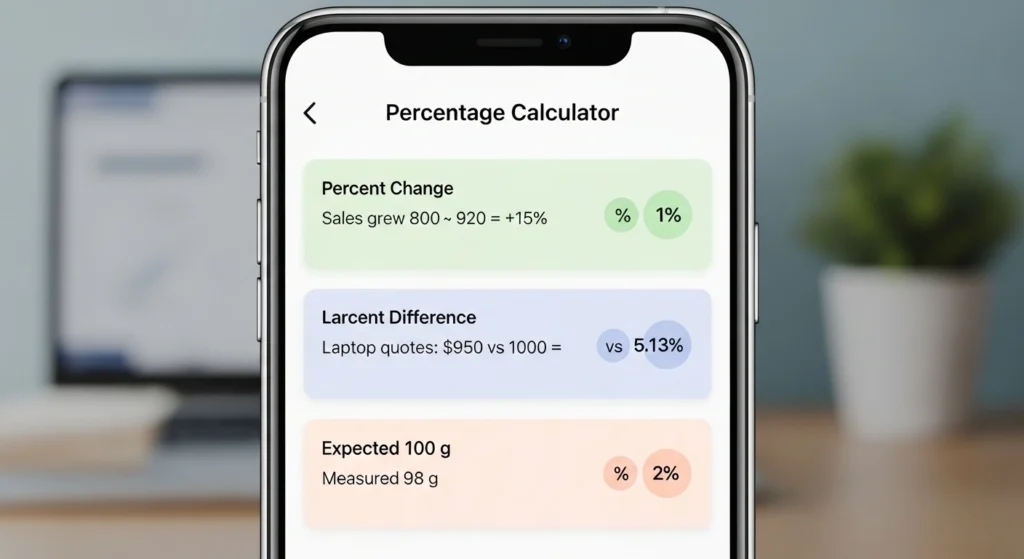
Percent change vs percent difference vs percent error
Use the right tool for the right question:
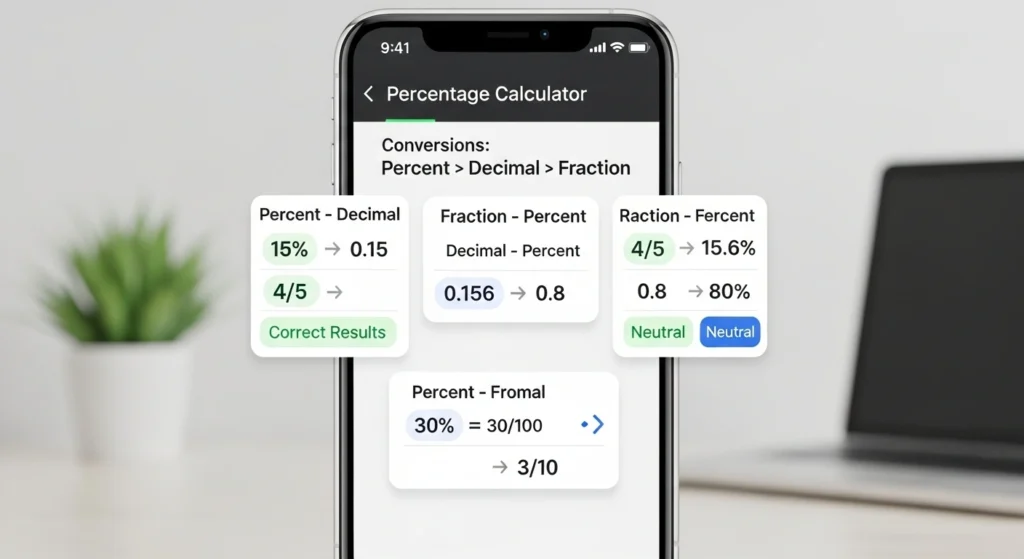
Conversions: percent ⇄ decimal ⇄ fraction
Percentage points (pp) vs percent (%)
Common pitfalls & pro tips

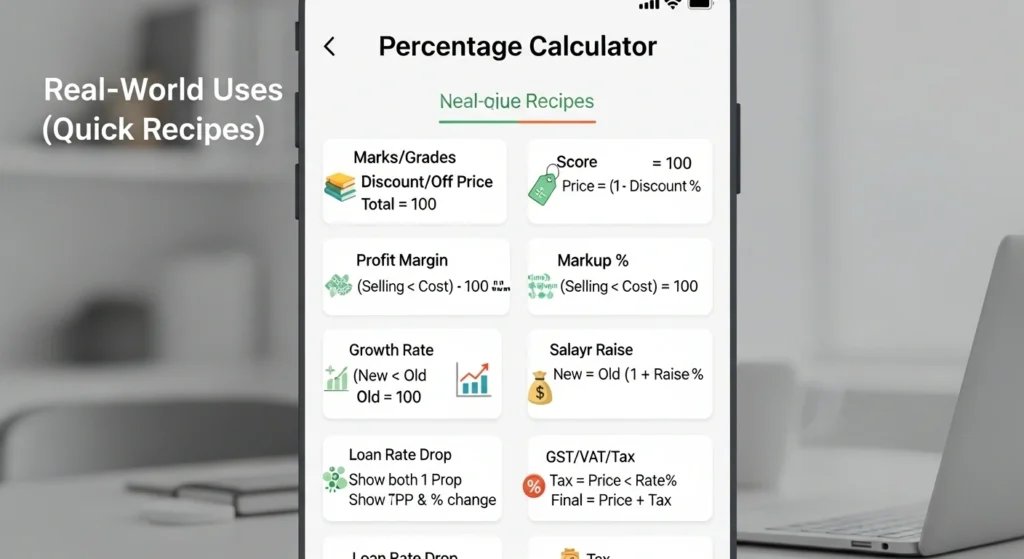
Real-world uses (quick recipes)
FAQs
Conclusion
Percentages power everyday decisions—from marks and salary to profit, growth, reduction, off price discounts, and loan comparisons. With the formulas above (and this calculator handling the math), you’ll move from guesswork to clarity in seconds using our percentage calculator. Bookmark this page, and use the four core modes to solve any percent question confidently.
Copy-ready snippet boxes (optional)
Percent of a number
Y = (P/100) × X
What percent is X of Y
P = (X ÷ Y) × 100
X is P% of what
Y = X ÷ (P/100)
Increase/Decrease by P%
New = X × (1 ± P/100)
Percent change
((New − Old) ÷ |Old|) × 100
Percent difference
|a − b| ÷ ((a + b)/2) × 100
Percent error
|Exp − Theo| ÷ |Theo| × 100
